Picato Gel
Picato Gel is a prescription, topical medication used to treat actinic keratosis. The drug was approved by the U.S. Food & Drug Administration (FDA) in 2012, and is marketed by Leo Pharmaceuticals. In 2015, the FDA required modifications to the Picato label, after it was linked to reports of severe allergic reactions, eye injuries and shingles.
Picato and Actinic Keratosis
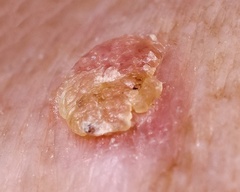 Actinic keratosis, also called solar keratosis, is a skin condition marked by a scaly, crusty lesion on the skin that may be red or yellow in color. These lesions are the result of sun-related damage, and typically appear on the face, bald scalp, lips, and the back of the hands. If the lesions are not treated, they may develop into a form of skin cancer called squamous cell carcinoma.
Actinic keratosis, also called solar keratosis, is a skin condition marked by a scaly, crusty lesion on the skin that may be red or yellow in color. These lesions are the result of sun-related damage, and typically appear on the face, bald scalp, lips, and the back of the hands. If the lesions are not treated, they may develop into a form of skin cancer called squamous cell carcinoma.
Derived from the sap of the milkweed plant, Picato gel was the first approved topical treatment for actinic keratosis. Picato 0.015% gel is applied to the face and scalp once a day for three consecutive days, while the more concentrated Picato 0.05% gel is applied to the trunk and extremities once a day for two consecutive days. Picato treats actinic keratosis by killing the cells that make up the scaly skin patch.
Picato Gel FDA Warning
In August 2015, the FDA disclosed that it had received reports of serious adverse events in patients treated with Picato gel. These adverse events included severe allergic reactions, eye injuries, and the reactivation of the herpes zoster virus (shingles). The reports prompted the FDA to order that the Picato label be modified to warn about these new safety risks and to provide additional instructions on the safe and appropriate application of the product.
The FDA is advising patients to use Picato gel as prescribed by their healthcare provider, and to avoid applying the product to a larger area of skin or for a longer time than instructed on the label. It’s also important to avoid applying the gel in, near, and around the mouth, lips and eye area, and to avoid accidental transfer of Picato from the hands. Accidental transfer can occur even after hand washing, especially during make-up application or contact lens insertion.
Symptoms of Picato allergic reactions, including anaphylaxis, generalized rashes, and contact dermatitis, may include:
- Throat tightness
- Difficulty Breathing
- Feeling faint
- Swelling of the lips or tongue
- Hives
- Itching
- Severe skin rash
Eye injuries that might be associated with the use of Picato Gel include:
- Eyelid swelling
- Eye irritation
- Pain
- Chemical conjunctivitis
- Corneal burns
Shingles reports associated with Picato gel included one case of ophthalmic herpes zoster in an immunocompromised patient.
- FDA (2012) “Picato Gel Drug Approval Package” http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2012/202833Orig1s000TOC.cfm
- FDA (2012) “Picato Gel Prescribing Information” http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2012/202833lbl.pdf
- FDA (2015) “Picato (ingenol mebutate) Gel: Drug Safety Communication – FDA Warns of Severe Adverse Events, Requires Label Changes” http://www.fda.gov/Safety/MedWatch/SafetyInformation/SafetyAlertsforHumanMedicalProducts/ucm459311.htm
- FDA (2015) “FDA Drug Safety Communication: FDA warns of severe adverse events with application of Picato (ingenol mebutate) gel for skin condition; requires label changes” http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DrugSafety/ucm459142.htm
Get the latest news and litigation updates about this case by following us on Facebook. Click the "Like" button below.
Follow Us


