Tasigna
Tasigna (nilotinib) is a cancer drug indicated to treat chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). Tasigna side effects may include arteriosclerosis, a potentially life-threatening condition that can lead to serious cardiovascular problems, amputations, and even death.
How Does Tasigna Work?
The U.S. Food & Drug Administration (FDA) initially approved Tasigna in October 2007 to treat Philadelphia chromosome positive chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) in adult patients resistant or intolerant to prior therapy that included imatinib. In October 2010, the FDA expanded Tasigna’s approved indications to include adult patients newly diagnosed with CML in chronic phase (CP-CML).
Tasigna is supplied as a 400 mg tablet, and is taken twice per day about 12 hours apart. Tasigna should be taken on an empty stomach.
Tasigna works by blocking a tyrosine kinase protein called Bcr-Abl, which is made by chronic myeloid leukemia cells that have an abnormal chromosome called the Philadelphia chromosome. Blocking Bcr-Abl protein stops the leukemia cells from growing.
Tasigna is taken for as long as it works. Tasigna patients undergo blood tests before and during treatment to monitor blood cell levels and other substances in the blood. They will also undergo tests to monitor kidney and liver function.
Tasigna Side Effects
The Tasigna prescribing information includes a Black Box Warning stating that the drug can elongate part of the heart’s rhythm (QT prolongation). The warning also notes that sudden death has been reported in patients, and cautions against using Tasigna in people with hypokalemia (low potassium levels), hypomagnesemia (low magnesium levels), or long QT syndrome. Finally, the Black Box Warning advises patients to avoid “use of concomitant drugs known to prolong the QT interval and strong CYP3A4 inhibitors,” and to avoid food 2 hours before and 1 hour after taking a dose of Tasigna.
Serious Tasigna side effects may include:
- QT prolongation
- Kidney problems
- Pancreas problems
- Liver problems
- Bone marrow suppression
- High or low potassium
- Low calcium
- Low sodium
- Bleeding in the brain
- Allergic reaction, difficulty breathing; swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat.
Common side effects may include:
- Diarrhea, constipation, stomach discomfort
- Mild itching or rash, temporary hair loss
- Runny or stuffy nose, sneezing, sore throat
- Mild headache, back pain, joint or muscle pain
- Fatigue
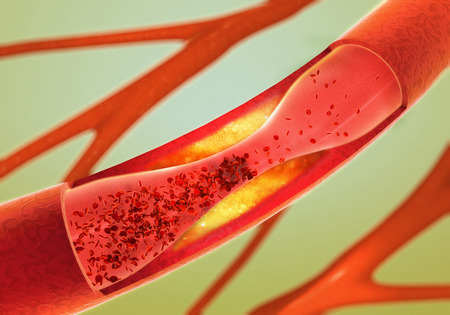
Tasigna and Arteriosclerosis
In April 2013, Health Canada issued an alert regarding a possible link between Tasigna and arteriosclerosis. Novartis also updated its Canadian product information sheets and warnings for Tasigna to include reference to the risk of potentially fatal atherosclerosis-related conditions.
While mention of arteriosclerosis was added to the Tasigna’s U.S. label, a public notification was never issued to doctors and patients in this country.
Arteriosclerosis is a hardening and narrowing of the arteries that slowly blocks these vital blood vessels. People with atherosclerosis are at risk for:
- Coronary heart disease (plaque in arteries in or leading to the heart)
- Angina (chest pain from reduced blood flow in arteries supplying the heart muscle),
- Carotid artery disease (plaque in neck arteries that supply blood to the brain)
- Peripheral artery disease (PAD; plaque in arteries of the extremities, especially the legs)
- Chronic kidney disease
- Amputations
- Heart attack
- Stroke
- Death
- FDA (2017) “Tasigna: Highlights of Prescribing Information” https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/022068s024lbl.pdf
- Health Canada (2013) “TASIGNA (nilotinib) – Possible Risk of Developing Atherosclerosis-Related Conditions – For the Public” http://healthycanadians.gc.ca/recall-alert-rappel-avis/hc-sc/2013/26659a-eng.php
- Heart Org (2017) “Atherosclerosis” http://www.heart.org/HEARTORG/Conditions/Cholesterol/AboutCholesterol/Atherosclerosis_UCM_305564_Article.jsp#.WXoKXYjytPY
Get the latest news and litigation updates about this case by following us on Facebook. Click the "Like" button below.
Follow Us


